Does Periodontal Disease Go Away – Real Facts You Need Today!
Many people worry when they hear the term “periodontal disease.” It is common to notice bleeding gums or bad breath and wonder if it means something serious. One of the most searched concerns today is does periodontal disease go away or does periodontal disease ever go away. This is important to understand because untreated gum problems often lead to more serious oral health issues. Gum disease affects more than just your mouth—it can also impact your overall health, including your heart and immune system.
If you are thinking about whether does periodontal disease go away after treatment, you are not alone. Millions of people worldwide face gum-related problems every year. The good news is that with early detection and proper care, many stages of periodontal disease can be reversed or controlled before they become worse.
This article explains in easy language what periodontal disease is, how it starts and spreads, and at which stages it can be reversed. It also includes personal experiences, signs and symptoms, prevention tips, and treatment options that can help manage this condition effectively.
What Is Periodontal Disease?
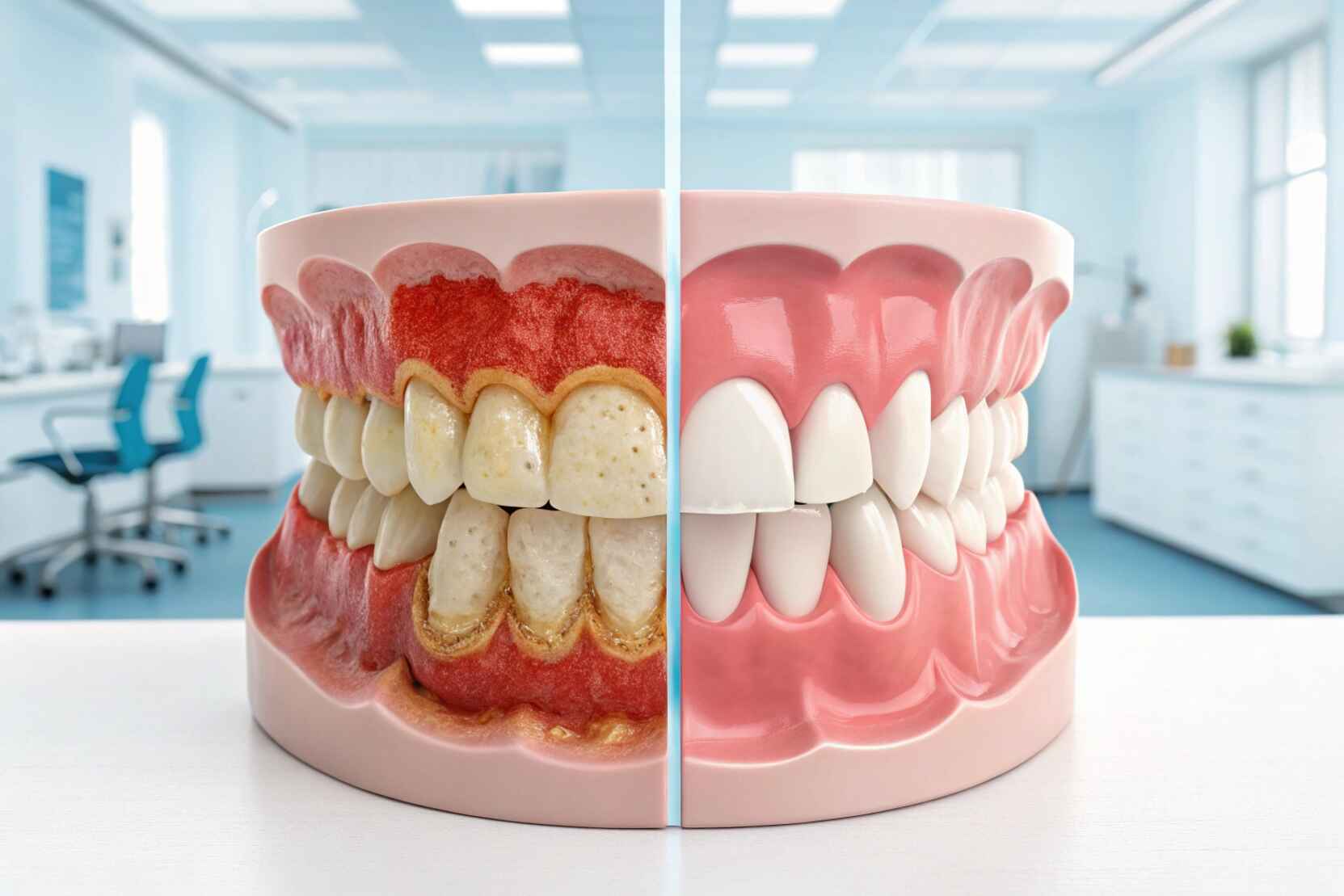
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and can destroy the bone supporting your teeth. It begins with mild symptoms like swollen gums, gum tenderness, and bleeding gums while brushing.
The early stage is called gingivitis, and it can be reversed with proper oral care. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe stage that causes tooth loss and other health problems. Maintaining gum health is very important to avoid these complications and keep your mouth free from gum infection and related issues.
Personal Experience With Gum Disease – Real Story and Recovery Tips!
A few years back, I began noticing blood on my toothbrush. I assumed I was brushing too hard and ignored it. Slowly, I also developed constant bad breath and gum soreness. A dental visit revealed I had early-stage gingivitis. That news made me take things seriously. I started flossing regularly, used an antibacterial mouthwash, and didn’t miss any dental cleanings.

Within months, my gums became healthier. This personal journey showed me how important early care is and why understanding questions like does periodontal disease go away and does periodontal disease ever go away matters for everyone dealing with gum health problems.
Why Is “Does Periodontal Disease Go Away” an Important Question?
Understanding does periodontal disease go away after treatment is an important question that can protect your health. Gum disease is not just about bleeding gums or bad breath. If ignored, it can lead to tooth loss, gum recession, and even serious health issues like heart disease. Many people fail to recognize early symptoms and delay treatment.
Early awareness allows you to take action before it’s too late. Knowing that gum disease is preventable and manageable helps reduce long-term damage and improves both your oral and overall health. Prevention always starts with awareness and care.
What Stages of Periodontal Disease Can Be Reversed?
Gingivitis – Is This Stage Reversible?
- Red, swollen gums
- Gums may bleed during brushing
- Bad breath
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is fully reversible. With good oral hygiene, such as brushing twice a day, flossing, and visiting the dentist regularly, the symptoms can completely go away. No permanent damage occurs if treated early, making this stage the easiest to handle.
Early Periodontitis – Can This Stage Be Managed?
- Gums begin to pull away from the teeth
- Mild bone loss starts
- Bad breath may persist
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is fully reversible. With good oral hygiene, such as brushing twice a day, flossing, and visiting the dentist regularly, the symptoms can completely go away. No permanent damage occurs if treated early, making this stage the easiest to handle. If you’re reading does periodontal disease go away reddit discussions, you’ll find many people sharing how gingivitis was cured with consistent care.
Moderate Periodontitis – Can You Reverse It?
- Gum pockets deepen
- Bone loss increases
- Gums may bleed frequently
Moderate periodontitis causes more advanced bone loss and gum damage. At this point, the disease is not reversible, but it can be controlled. Dentists focus on stopping the progression with professional treatments. Maintaining oral hygiene and regular checkups are essential to managing this stage and preventing it from worsening.
Severe Periodontitis – Is This the End Stage?
- Teeth become loose or shift
- Severe gum recession
- Serious bone loss
Severe periodontitis is the final and most damaging stage. The gums and bone holding your teeth are severely affected. This stage cannot be reversed, and the main goal is to stop further damage. Tooth extractions, surgery, or ongoing specialist care may be required to maintain function and comfort. Even with dentures, it’s crucial to remember that does periodontal disease go away with dentures is a real question—dental prosthetics don’t cure infection, they just replace teeth.
What Happens If You Don’t Treat Any Stage?
- Tooth loss becomes likely
- Gums stay inflamed and infected
- Jawbone can shrink over time
If left untreated, gum disease continues to damage both soft and hard tissues in the mouth. You may experience tooth loss, gum pain, jawbone damage, and even increased risk of heart issues. Treating gum disease early can help you avoid painful, costly procedures and maintain better oral health for life.
Periodontal Disease Stages and Reversibility – Find Out What’s Reversible!
| Stage | Can It Go Away? | Treatment Required | LSI Terms Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Yes | Brushing, flossing, cleanings | Gum inflammation, bleeding gums, does periodontal disease ever go away |
| Early Periodontitis | No (but controllable) | Deep cleaning, improved hygiene | Mild bone loss, plaque buildup, does periodontal disease go away after treatment |
| Moderate-Severe Periodontitis | No | Surgery, antibiotics, maintenance | Loose teeth, gum pockets, infection, does periodontal disease go away reddit |
Cure or Manage Does Periodontal Disease Go Away Completely – Simple Steps to Take Now!
- Early stage (gingivitis): Yes, gingivitis can go away completely. With proper brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings, the gums heal and return to normal. Early action is important to stop the disease before it turns into something more serious like periodontitis.
- Advanced stage (periodontitis): No, it does not go away, but it can be managed. Treatment can stop the condition from getting worse. Regular deep cleanings, dentist visits, and strong oral care habits at home are needed to keep it under control long term.
- No cure without treatment: Many people think it heals naturally, but that’s incorrect. Periodontal disease requires dental treatment. Ignoring the symptoms lets it spread and cause lasting damage. Early care gives the best chance to control or reverse the early stage of the disease.
- Professional help is key: Dentists use procedures like scaling and root planing to clean under the gums. They can slow down the disease and reduce symptoms. Regular follow-ups are needed to check progress. Without this care, the disease usually continues to get worse.
- Home care matters: Brushing twice a day, flossing, and using mouthwash help a lot. These habits keep plaque under control and support dentist treatments. Skipping daily care makes it hard to manage gum disease, even with professional help. Personal effort plays a big role.
What Are the Treatment Options for Mild to Advanced Periodontitis?
Mild (Gingivitis):
Mild gum disease, called gingivitis, can be treated by brushing and flossing regularly. Using an antibacterial mouthwash helps reduce bacteria. Professional dental cleanings remove plaque and tartar that home care misses. These steps usually stop gingivitis and help gums heal before the disease progresses.
Moderate Periodontitis:
In moderate periodontitis, gums start pulling away from teeth. Dentists perform scaling and root planing to clean deep below the gum line. Antibiotic gels may be applied to fight infection. While it can’t be fully reversed, treatment controls damage and prevents further progression when combined with good home care.
Severe Periodontitis:
Severe periodontitis requires advanced treatment like surgery to clean infected areas or bone grafts to restore lost bone. Laser treatment can remove diseased tissue with less pain. New treatments include antibiotic chips and topical gels placed in gums. These help control infection and save teeth but do not cure the disease completely.
Lifestyle and Risk Factors That Impact Periodontal Health – See List!
Certain lifestyle choices and health conditions can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease. Smoking or using tobacco is one of the biggest risk factors, as it weakens the gums and immune system. Diabetes also raises the chance of gum problems because it affects blood flow and healing.
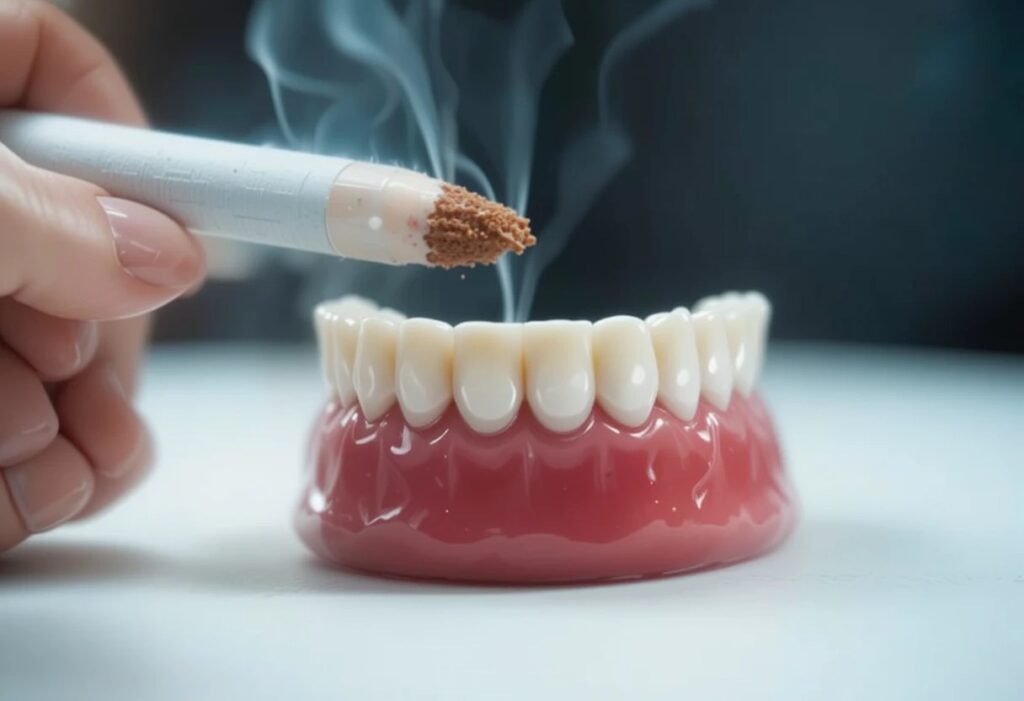
Poor diet, high stress levels, and hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can harm gum health too. Genetics play a role, making some people more prone to gum disease. Understanding these periodontal risk factors helps in preventing and managing gum health effectively.
How Can You Manage Periodontal Disease Long-Term?
Even though periodontal disease may not completely go away, it can be effectively controlled with proper care. To manage it long-term, brush your teeth twice daily using a soft-bristled brush to avoid irritating gums. Floss every day to remove plaque between teeth.
Using an antibacterial mouthwash helps reduce harmful bacteria. Regular dental visits every 3 to 6 months are important for professional cleaning and monitoring. Avoid tobacco products, as they worsen gum health. For diabetic patients, controlling blood sugar levels is essential. Staying consistent with these habits prevents bacteria from growing and keeps gum disease under control.
Easy Ways to Prevent Periodontal Disease – Avoid Gum Problems Early!
- Maintain oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss once a day. This removes plaque and food particles, helping to keep your gums healthy and prevent early signs of gum disease from developing further.
- Eat a healthy diet: A balanced diet supports your immune system and gum health. Include leafy greens, fruits, and foods rich in Vitamin C. Avoid processed and sugary items, which feed harmful bacteria and contribute to inflammation and gum infections.
- Avoid sugary snacks and drinks: These can lead to more plaque, which causes gum irritation and infection. Switch to healthier snacks like fruits, yogurt, or nuts, and drink water often to wash away bacteria and food particles after eating.
- Quit smoking: Tobacco damages your gums, lowers healing ability, and increases your risk for periodontal disease. Quitting smoking improves blood flow to your gums and makes oral care treatments more effective in preventing further gum damage.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Get dental check-ups every six months or as advised. Professional cleaning removes hardened plaque (tartar) that brushing can’t. Early detection of gum problems means better results and a higher chance of reversing early gum disease..
When to See a Dentist or Periodontist?
It’s important to see a dentist before gum disease gets worse. Many early signs are painless, so people often ignore them. You should visit a dentist if your gums bleed often, look red or swollen, or if you have ongoing bad breath. Loose teeth and gums pulling away from your teeth are also warning signs. These may show that gum disease is progressing.
A regular dentist can help in early stages, but for more serious cases, a periodontist—a gum disease specialist—may be needed for deeper cleaning or advanced treatment. Early checkups can save teeth and prevent costly treatments. Don’t wait for pain—it may already be too late.
FAQs:
1. How long can periodontal disease last?
Periodontal disease can last a lifetime if not treated. It progresses slowly, often without pain, making it easy to ignore. However, with proper treatment, dental care, and healthy habits, it can be managed effectively. Regular checkups and good oral hygiene can stop it from getting worse and help protect your teeth and gums. Many wonder does periodontal disease ever go away, and while early stages can, advanced stages require lifelong care.
2. Can your gums heal from periodontal disease?
Your gums can fully heal from gingivitis, which is the early stage of periodontal disease. But if it has progressed into periodontitis, the damage cannot be completely reversed. However, treatment can reduce inflammation, control infection, and prevent further damage. With ongoing care, your gums can stay healthy and stable over time. This is a popular topic on does periodontal disease go away reddit.
3. How do you stop periodontitis from progressing?
To stop periodontitis from getting worse, follow a strong oral hygiene routine. Brush twice daily, floss every day, and use an antibacterial mouthwash. Avoid smoking, manage health conditions like diabetes, and visit your dentist every 3–6 months. These steps help remove harmful bacteria and reduce gum inflammation, keeping the disease under control.
4. Can you reverse periodontal disease?
You can reverse periodontal disease only if it’s still in the early stage—gingivitis. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental cleanings can completely heal gingivitis. However, once it turns into periodontitis, it cannot be reversed. Still, it can be managed with professional care to stop further bone and tissue loss around your teeth. If you’re asking does periodontal disease go away after treatment, remember it depends on the stage.
5. Can I save my teeth with periodontal disease?
Yes, you can save your teeth if you catch the disease early and follow your dentist’s treatment plan. Even with periodontitis, deep cleanings, medications, and lifestyle changes can protect your teeth. The key is consistency—brush, floss, avoid tobacco, and get regular dental care to prevent tooth loss and preserve your smile. Even if you wear dentures, does periodontal disease go away with dentures is a question worth asking, because gum health remains essential.
Conclusion:
Periodontal disease is a serious gum condition that needs early attention to avoid long-term damage. Gingivitis, the early stage, can be fully reversed with proper oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings. However, once it progresses to periodontitis, it cannot be cured—only managed.
Consistent care, including brushing, flossing, dental visits, and lifestyle improvements like quitting smoking, can help control the disease. Taking early action is key to saving your teeth, protecting your gums, and maintaining your overall health. Prevention and timely treatment make a big difference in long-term gum health.
Related post: