Can Gum Disease Be Reversed – The Truth About Saving Your Gums Fast!
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth. It develops due to poor oral hygiene, plaque buildup, and other health factors. Early stages may go unnoticed, but over time, it can lead to serious dental problems, including tooth loss.
Understanding its causes, symptoms, and stages is important for proper treatment. Reversing gum disease is possible in some cases, particularly when it is detected early. This article explains the condition and offers helpful tips on treatment and prevention for better oral health.
What is Gum Disease?
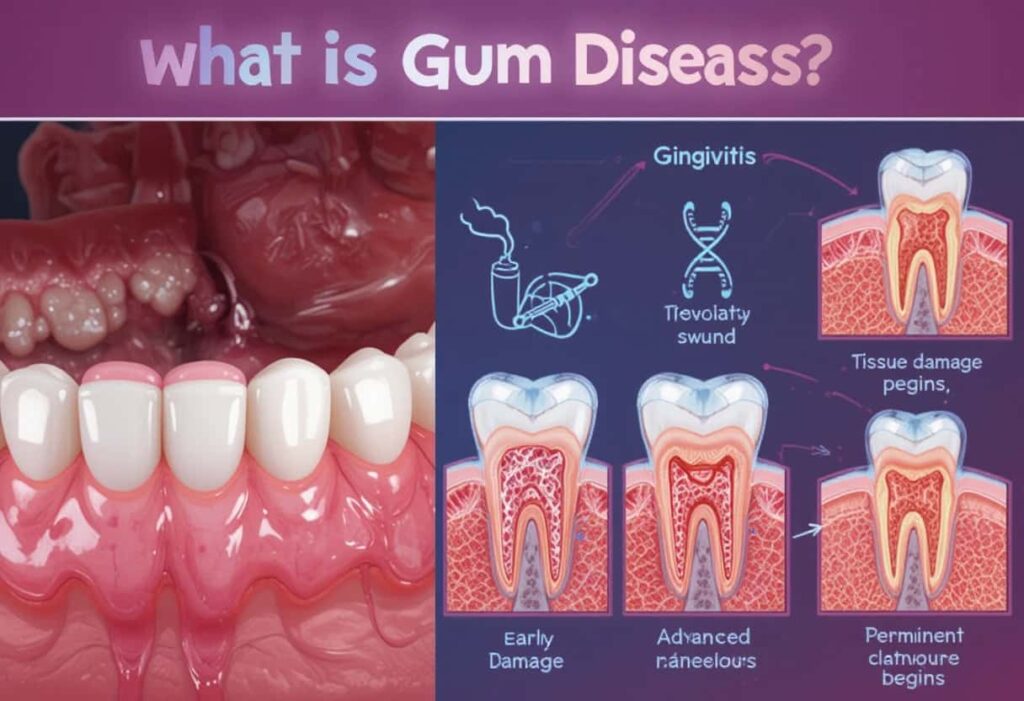
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. It usually starts as inflammation of the gums and can progress to damage the bone beneath your teeth. Poor oral hygiene is the main cause, but factors like genetics and health conditions can increase risk.
It often begins with redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, especially during brushing. If left untreated, it can lead to loose teeth or even tooth loss. Smoking, diabetes, and hormonal changes can also make the condition worse. Regular dental check-ups are essential to catch it early.
What Are the Types and Stages of Gum Disease?
Gum disease develops in different stages, each with increasing severity. Understanding these stages helps in early detection and effective treatment. From mild inflammation to serious bone damage, each stage requires specific care to manage or prevent permanent damage
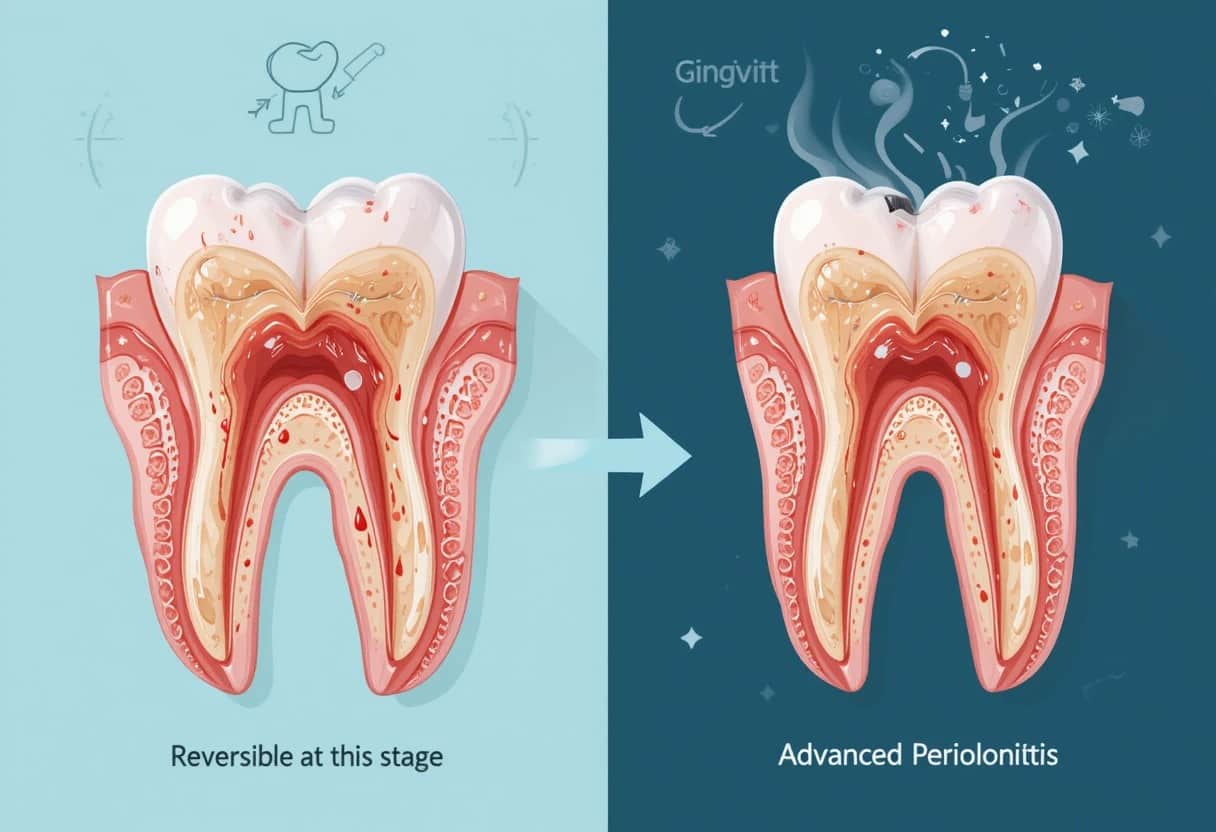
Gingivitis – The Reversible Stage!
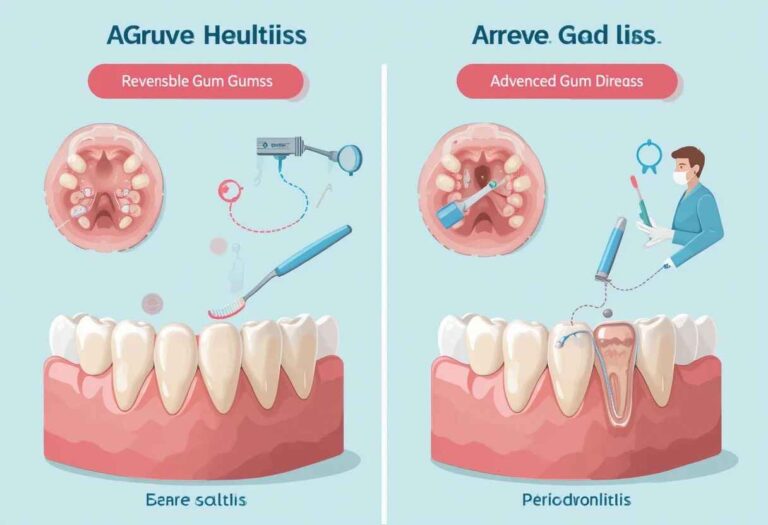
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease. It causes red, swollen, and bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing. There is no bone loss at this point, making it fully reversible. With daily brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, gingivitis can be treated effectively and prevented from progressing to more serious stages.
Mild Periodontitis:
This stage marks the early progression from gingivitis. Bacteria travel below the gum line, forming pockets around the teeth. These pockets begin to destroy the supporting bone. While dental treatment can stop further bone loss, reversing the existing damage is difficult. Good oral hygiene and routine dental visits are critical at this point.
Moderate Periodontitis:
Moderate periodontitis involves deeper infection and greater bone and ligament damage. Symptoms may include persistent bad breath, visible pus, gum recession, and loose teeth. Treatment may include scaling and root planing. Though the condition can be controlled, lost bone and support structures usually cannot be regained fully. Long-term maintenance is necessary.
Advanced Periodontitis:
This is the most severe stage, with significant bone loss, deep gum pockets, and possible tooth loss. Gums may recede greatly, and teeth may shift or fall out. Treatment aims to control infection and prevent further deterioration. Surgical procedures may help improve function, but full recovery of bone and tissue is unlikely.
Also read: Arranie Healthsciencesforum – Connect, Learn, Succeed!
Can Gum Disease Be Reversed?
Reversal Is Possible in Early Stages:
In the early stage, known as gingivitis, gum disease is completely reversible. At this point, there is no bone loss. With professional dental cleaning, proper brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups, the gums can return to a healthy state. Consistent oral hygiene plays a key role in stopping the inflammation and restoring gum health.
Management, Not Reversal, in Advanced Stages:
In moderate to advanced stages, gum disease causes permanent damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth. While it cannot be fully reversed, it can be managed through deep cleaning, medications, or even surgery. These treatments help reduce infection, tighten gums, and prevent further bone loss, helping you maintain oral health and avoid tooth loss.
Why Reversal Becomes Difficult?
Once bone and tissue are lost, natural regeneration is limited. Treatment focuses on infection control and minimizing damage. The body cannot fully rebuild lost bone around teeth without special procedures. Advanced stages may require surgery, like grafts or flap surgery.
Even then, results depend on the severity of the damage and overall oral health. Healing also varies from person to person. Delayed treatment makes the condition harder to control. Consistent follow-up care is crucial to avoid further complications.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gum Disease – Experts Reveal the Biggest Triggers!
- Main Cause: Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If not removed, it hardens into tartar. Tartar irritates the gums and causes inflammation, leading to gum disease.
- Impact of Smoking: Smoking or using tobacco products weakens the immune system. It makes it harder for gums to heal and increases the risk of developing gum disease.
- Health Conditions and Risk: Diabetes and autoimmune diseases reduce the body’s ability to fight infections. These conditions raise the chance of gum disease and make treatment more difficult.
- Hormones and Genetics: Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can increase gum sensitivity. Genetics also play a role, making some people more prone to gum disease than others.
- Oral Hygiene and Other Factors: Poor oral hygiene allows plaque buildup. Stress and certain medications can affect gum health, increasing the risk of infection and gum disease progression.
What Causes Bad Breath and Gum Problems?
Red, Swollen, or Bleeding Gums:
One of the first signs of gum disease is red, swollen, or bleeding gums. This happens because plaque buildup causes irritation and inflammation. If you notice bleeding while brushing or flossing, it means your gums are sensitive and need attention. Early detection helps prevent the disease from worsening.
Persistent Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste:
Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth can be a sign of gum infection. Bacteria trapped in gum pockets produce foul odors. Even after brushing, this unpleasant smell may remain. If you experience this regularly, it is important to get your gums checked by a dental professional.
Pain While Chewing:
Pain or discomfort during chewing might indicate that gum disease is affecting your teeth or gums. Infection and inflammation can make eating uncomfortable. Ignoring this pain could lead to more serious problems like loose teeth or abscesses. Timely dental care can relieve pain and stop the disease’s progress.
Gum Recession and Loose Teeth:
Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing roots. This happens as gum disease worsens and damages supporting tissues. Loose teeth indicate that the bone and ligaments holding the teeth are affected. Both symptoms show advanced gum disease and require immediate dental treatment to save your teeth.
Changes in Bite or Teeth Alignment:
As gum disease damages the tissues supporting teeth, it can cause changes in your bite or how your teeth fit together. Teeth may shift or become misaligned, making chewing difficult. This problem worsens if left untreated and may require dental procedures to correct bite issues and restore oral health.
Importance of Early Symptoms:
Noticing early symptoms like bleeding gums is important because it allows for quick treatment. Early care can reverse gum disease before it causes serious damage. Delaying dental visits may lead to permanent harm and more complex treatments. Regular dental checkups help catch problems early and keep your gums healthy.
Also read: Does Periodontal Disease Go Away – Real Facts You Need Today!
How to Protect Your Teeth Effectively – Diagnosis of Gum Disease!

- Visual Exam: Dentists look closely at your gums for redness, swelling, and plaque buildup. These signs help identify early gum disease and decide if further tests are needed to confirm the condition.
- Gum Pocket Measurement: Using a small probe, the dentist measures the space between your gums and teeth. Deeper pockets often mean more severe gum disease, helping guide the right treatment approach.
- X-rays: Dental X-rays show the bone levels around your teeth. Loss of bone indicates advanced gum disease and helps the dentist understand how far the infection has spread.
- Tooth Looseness Check: The dentist gently tests if your teeth are loose or moving. Loose teeth suggest damage to the tissues and bone supporting them due to gum disease.
- Gum Recession: The dentist checks if gums have pulled away from teeth, exposing roots or tooth surfaces. This can signal worsening gum disease and the need for immediate care.
Treatment Options to Reverse or Manage Gum Disease – Expert Tips for Healthier Gums!
Professional Dental Cleaning:
Professional dental cleaning is crucial for treating gingivitis and mild gum disease. It involves removing plaque and tartar buildup that irritate the gums and cause inflammation. Regular cleanings help reverse early gum disease when combined with proper daily oral hygiene. This process restores gum health, prevents further damage, and reduces the risk of progression to more serious stages of gum disease.
Scaling and Root Planing:
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure used for mild to moderate periodontitis. It removes bacteria, plaque, and tartar from below the gum line, where regular cleaning can’t reach. The tooth roots are then smoothed to prevent new plaque buildup. This treatment reduces gum pocket depth, decreases inflammation, and helps stop further damage to the gums and supporting bone.
Pocket Reduction Surgery:
Pocket reduction surgery is recommended when gum pockets become too deep for effective cleaning. The dentist surgically removes bacteria and infected gum tissue beneath the gum line. This procedure reduces the size of the pockets, allowing the gums to better attach to the teeth. It helps control the infection, improve gum health, and prevent further bone and tissue loss in advanced cases.
Laser Therapy (LANAP):
Laser therapy, such as LANAP, is a minimally invasive treatment option for gum disease. It uses laser energy to selectively remove infected gum tissue without harming healthy tissue. The laser sterilizes the area and promotes faster healing, reducing discomfort and bleeding. This method reduces bacteria and inflammation, making it an effective alternative or addition to traditional gum disease treatments.
Bone and Gum Grafting:
Bone and gum grafting are surgical treatments used in advanced gum disease to restore lost tissues. Bone grafting replaces bone that has been destroyed by infection, helping to stabilize teeth. Gum grafting restores receded gums to protect exposed tooth roots and improve oral appearance. These procedures support tooth stability and overall gum health, improving long-term dental outcomes.
Regenerative Procedures:
Regenerative procedures, including guided tissue regeneration and platelet-rich plasma therapy, promote the healing and partial regrowth of lost bone and gum tissue. These advanced treatments stimulate the body’s natural ability to repair damage caused by periodontitis. By encouraging tissue regeneration, these therapies help rebuild the supporting structures of teeth, improving oral health and increasing the chances of saving natural teeth.
Also read: Is Gum Disease Reversible – But Only If You Act Fast!
Prevention of Gum Disease – Best Practices to Avoid Gum Problems!
- Daily Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth two to three times a day to remove plaque. Floss daily to clean between teeth where brushes can’t reach. Use antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen breath.
- Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking or using tobacco products as they weaken gums. Manage diabetes and other health issues that increase gum disease risk. Keep stress low to support your immune system.
- Regular Dental Visits: Visit your dentist every six months for check-ups and professional cleanings. Those with higher risk may need more frequent visits to monitor and prevent gum disease.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to strengthen your gums and immune system. Limit sugary foods that encourage plaque formation.
- Long-Term Outlook: Consistent prevention helps maintain healthy gums and avoid serious dental problems. Early care can stop gum disease before it causes permanent damage.
Long-Term Outlook for Gum Disease Patients – Tips to Protect Your Smile!
While gum disease cannot be completely cured, early diagnosis and treatment allow for effective management. Good oral hygiene and professional care can prevent tooth loss and improve overall health. Gum disease has also been linked to serious conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, making treatment important beyond oral health.
Maintaining regular dental visits helps monitor gum health and catch any problems early. Patients who follow treatment plans experience better outcomes and reduced complications. Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking and managing chronic illnesses also support long-term gum health.
How Do You Live with Gum Disease?
If you notice symptoms like bleeding or swollen gums, see your dentist quickly. With ongoing care, you can control the disease and keep your smile healthy. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential to prevent progression. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco, also supports gum health. Early action and consistent care make a big difference in managing gum disease.
It’s important to follow your dentist’s advice and complete any prescribed treatments. Managing stress and staying hydrated can also help your gums heal. Staying informed about your oral health encourages better habits and outcomes.
FAQs:
1. Can gum disease be life-threatening?
Gum disease itself is not usually deadly, but advanced periodontitis can increase the risk of serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. These conditions can be life-threatening. Treating gum disease early helps reduce inflammation and lowers the risk of these severe complications.
2. How can I treat gum disease without visiting a dentist?
Mild gum disease, like gingiviti,s may improve by brushing twice daily, flossing, and using antibacterial mouthwash. Avoid tobacco and maintain a healthy diet. However, professional dental care is important for removing tartar and preventing further damage. Without a dentist’s help, gum disease may worsen over time.
3. How fast can gum disease worsen if untreated?
Gum disease can progress quickly from mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis within weeks or months if untreated. The infection spreads below the gum line, causing bone loss and tooth loosening. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to stop progression and save teeth.
4. Does gum disease increase cancer risk?
Chronic gum infection and inflammation may slightly increase the risk of some cancers, especially oral cancers. The ongoing inflammation caused by bacteria can affect overall health. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can help reduce these risks.
5. What are the main types of gum disease?
The two main types of gum disease are gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis causes gum redness, swelling, and bleeding, but is reversible with good care. Periodontitis is more serious, causing damage to the bone and tissues supporting teeth, which can lead to tooth loss if untreated.
Conclusion:
Gum disease can be reversed primarily in its earliest stage, known as gingivitis, where inflammation affects only the gums without any bone loss. With proper daily brushing, flossing, regular professional cleanings, and dental check-ups, the inflammation can be stopped, allowing the gums to heal and return to a healthy state.
However, once gum disease advances to periodontitis, causing damage to the bone and supporting tissues, full reversal is challenging. At this stage, treatment focuses on controlling infection and preventing further damage, often requiring deep cleaning or surgery to preserve oral health. Early detection and consistent care are crucial for the best outcomes.
Related post: