Do Ants Carry Disease – Stay Safe Now!
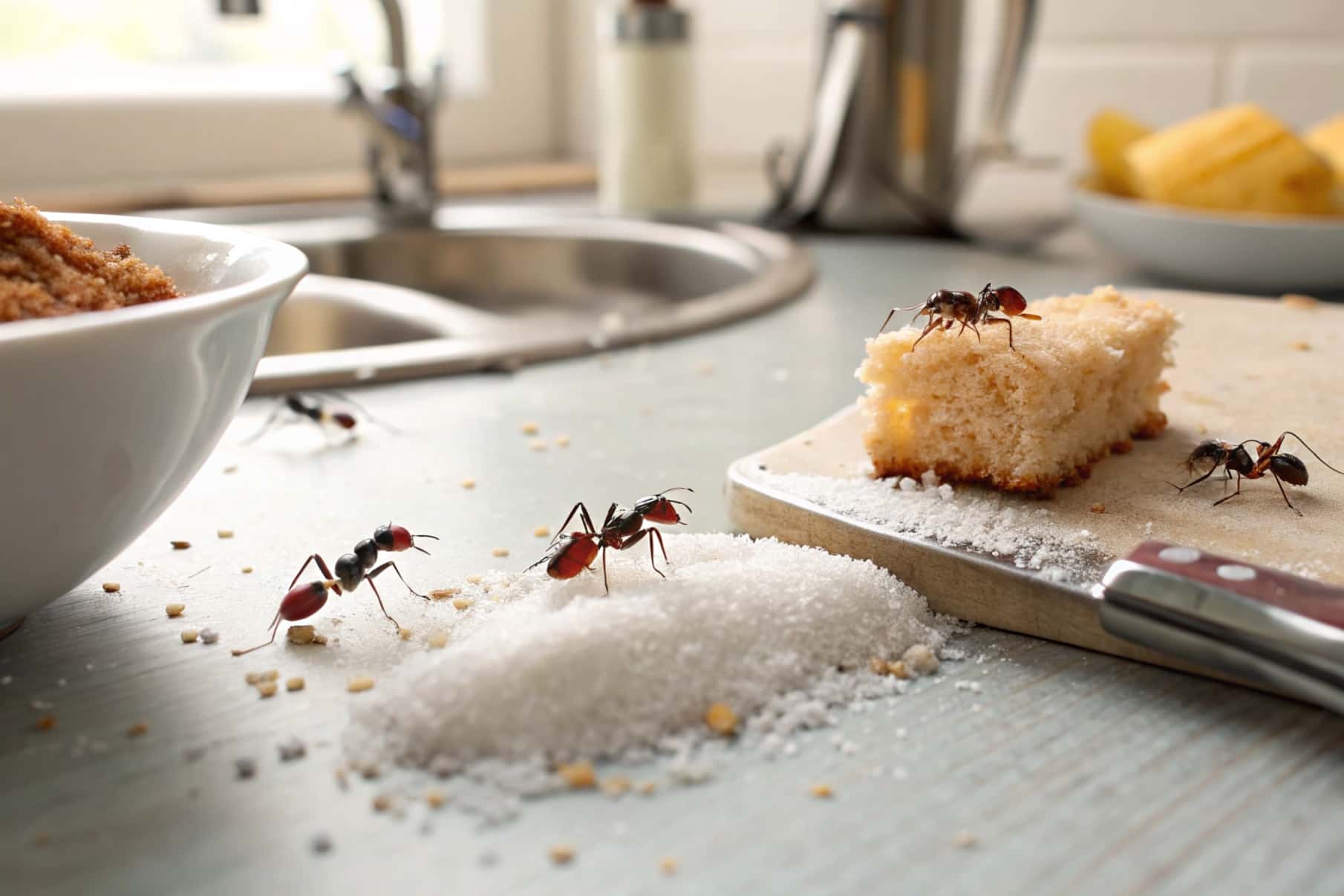
Ants are small insects commonly found in homes, gardens, and workplaces. Although they do not spread diseases as directly as mosquitoes or ticks, do ants carry any diseases? The answer is yes, but indirectly. Ants can still pose certain health risks. They can carry and transfer harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli from dirty areas to food and surfaces. This movement can lead to contamination and potential foodborne illnesses.
Additionally, some ants, such as fire ants, can bite or sting, causing allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Knowing how ants impact health is important for preventing infestations and protecting your family. Taking early action can help avoid larger problems down the line.
What Are the Health Risks of Ants?
To begin with, it’s important to understand that ants are not traditional disease carriers like some other pests. However, they do have the ability to pick up and transport harmful bacteria and pathogens as they move around. This means ants can be indirect carriers of illnesses, especially if they contaminate your food or surfaces in your home.

Ants live in colonies that can grow quickly, which means a small problem can turn into a big one if left untreated. They often invade kitchens, pantries, and bathrooms — places where bacteria thrive. So, even though ants themselves aren’t sick, they can bring harmful germs along with them.
How Long Do Ants Live and Why Does It Matter?
Understanding the lifespan of ants can help you realize how long an infestation may last. Worker ants typically live for a few months, but queen ants can live for several years, continuously producing new ants. This means an infestation can persist and grow if not controlled.
Because ants reproduce quickly and are hard to see, they can contaminate your home for a long time before you notice a problem. Early action is important to stop the spread of bacteria and reduce health risks.
Are Ants a Health Hazard in Your Home?
Yes, ants can be a health hazard in your home, even though they aren’t known to transmit diseases like mosquitoes or ticks. Ants often travel through unsanitary areas such as garbage bins, drains, and toilets before crawling onto kitchen counters, food storage, and dining surfaces—spreading harmful bacteria like salmonella, E. coli, and staph.
Some species also carry foodborne pathogens from outside environments. Additionally, ant bites can cause allergic reactions, infections, and skin irritation. Eliminating infestations promptly is essential to protect your household from potential health risks caused by ant activity.
How Do Ants Spread Bacteria Throughout Your Home?
Travel Through Contaminated Areas: Ants often crawl through toilets, trash bins, and drains where harmful bacteria are present.
Carry Germs on Their Bodies: As ants move, they transport bacteria on their legs and bodies from dirty to clean surfaces.
Contaminate Food and Utensils: Ants can quickly spread bacteria to food, dishes, and kitchen tools just by walking over them.
Infest Food Storage Areas: If ants access pantries or cabinets, they can contaminate sealed or unsealed food with pathogens.
Transfer Bacteria Indoors: Ants coming from outside may bring environmental pathogens like E. coli, salmonella, or fungi into the home.
How Do Ants Spread Bacteria and Illness?
When you think about how ants travel, it’s clear why they can be a problem. Ants are scavengers, moving between garbage, dirty areas, and your clean food. This movement allows them to pick up bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, Staphylococcus, and others. When ants move from contaminated areas to your food or kitchen counters, they can leave behind these germs.
For example, if an ant walks over a trash bin full of spoiled food and then moves to your dining table, it can transfer bacteria to the surfaces you touch and the food you eat. This process is called cross-contamination.
Also read: Arranie Healthsciencesforum – Connect, Learn, Succeed!
What Diseases Can Ants Carry?
Although ants don’t carry diseases the same way mosquitoes transmit malaria or dengue, they can carry several types of foodborne pathogens. Here are some of the main illnesses linked to ants:
| Disease or Pathogen | How Ants Spread It | Possible Symptoms |
| Salmonella | By walking on contaminated food | Diarrhea, fever, stomach cramps |
| E. coli | Transferring bacteria to food | Severe stomach cramps, vomiting |
| Staphylococcus | From dirty surfaces to food | Food poisoning, skin infections |
| Shigella | Carrying from waste to food | Diarrhea, fever, stomach pain |
| Clostridium | Transferring spores to food | Food poisoning |
These bacteria can cause food poisoning and other infections, especially in children, elderly people, and those with weak immune systems.
How do ants pose health risks through disease transmission, bites, and food contamination in human environments?
Transmission of Harmful Pathogens:
Ants can carry and transmit bacteria such as Salmonella, Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus. These pathogens are picked up as ants travel through contaminated areas like garbage bins, drains, and restrooms, then transferred to food, utensils, and preparation surfaces, increasing the risk of foodborne illness and cross-contamination within homes and commercial kitchens.
Hospital Infestations:
Pharaoh ants are particularly dangerous in healthcare settings. They’re attracted to IV fluids and open wounds in burn units, potentially spreading harmful organisms like Clostridium and causing serious infections. Their tiny size allows them to invade sterile environments, posing significant health threats to immunocompromised and recovering patients.
Food Contamination:
As ants forage for food and moisture, they often walk through unclean areas and carry bacteria back to pantries, countertops, and food containers. This behavior introduces harmful microbes like E. coli and Shigella to clean surfaces, contributing to the spread of foodborne illnesses among household members or restaurant patrons.
Bites and Venom Allergies:
While ants aren’t major disease vectors like mosquitoes, their bites and stings—especially from fire ants—can trigger allergic reactions. In sensitive individuals, this may cause pain, swelling, or even life-threatening anaphylaxis. Without proper care, bites can also become infected, adding another layer of health concern.
Overlooked Health Risks in Homes:
Most homeowners view ants as mere nuisances, but their foraging behavior can introduce pathogens into bathrooms and kitchens. By transferring germs from dirty areas to clean ones, they pose subtle yet serious risks. Understanding this helps emphasize the importance of ant control and good hygiene practices indoors.
Can Ants Cause Foodborne Illnesses in Your Kitchen?
Yes, ants can cause foodborne illnesses in your kitchen. As they move through unsanitary areas like drains, garbage bins, and bathrooms, ants pick up harmful bacteria such as salmonella, E. coli, staphylococcus, and shigella. When they crawl across kitchen counters, food containers, or inside pantries, they can transfer these pathogens to your food and cooking surfaces.
Even sealed foods can be at risk if ants contaminate utensils or prep areas. This makes ant infestations not just a nuisance—but a genuine health concern, especially for children, the elderly, or those with weakened immune systems.
Can Ants Transmit Disease to Humans?
Yes, do ants carry diseases that affect humans? Ants can indirectly transmit diseases to humans. While they don’t cause illnesses themselves, ants often carry harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli on their bodies. When they move from dirty places to your food or surfaces, they can spread these bacteria, increasing the risk of food poisoning and infections.
So, although ants are not direct disease carrier like some insects, their presence can still pose a health concern if infestations are not managed properly. This is why maintaining cleanliness and controlling ant populations in your home is important for reducing potential health risks. Additionally, some ant species can bite or sting, which may cause allergic reactions or infections in sensitive individuals.
Can Ant Bites or Stings Cause Health Problems?
Many people wonder if ant bites or stings are dangerous. The truth is, most ants only bite when they feel threatened, and the bite is usually more annoying than dangerous. However, some ants like fire ants have venomous stings that can cause serious allergic reactions.
Here’s what to expect from an ant bite or sting:
- Mild bites: Redness, swelling, and itching.
- Allergic reactions: Severe swelling, rash, or difficulty breathing (rare but serious).
- Infections: If the bite breaks the skin and bacteria enter, it can lead to infections like cellulitis.
If you have a known allergy to insect stings, it is important to seek medical attention if bitten by ants.
Also read: What Is Dis-Ease – Real Signs And Hidden Causes!
How Can You Prevent Ants from Spreading Disease?
Preventing ants in your home is the best way to avoid the health risks they bring. Here are some practical tips:
- Keep food sealed and stored properly. Use airtight containers to protect your pantry items.
- Clean kitchen surfaces regularly. Wipe counters, sinks, and floors to remove food residues.
- Take out the trash frequently. Ants are attracted to garbage, so keep bins covered and emptied.
- Fix leaks and moisture problems. Ants need water, so dry wet areas in your home.
- Seal entry points. Close cracks and holes where ants can enter.
What Should You Do If You Have an Ant Infestation?
If you notice ants in your home, it’s important to act quickly. While DIY methods like sprays and baits can help, they often don’t solve the problem completely. Ant colonies are complex and may hide in walls or underground.
Professional pest control services have the knowledge and tools to find the source of the infestation and treat it effectively. They can create barriers to keep ants out and use safe methods to eliminate them.
Also read: What To Feed A Dog With Inflammatory Bowel Disease – Best Diet Tips That Work!
Are All Ant Species a Health Threat?
Not all ants pose the same risk. Here are some common types of ants and their health impact:
- Sugar ants: Attracted to sweet foods, they can spread bacteria in kitchens.
- Carpenter ants: They do not eat wood but tunnel into it, potentially damaging your home. They can also carry bacteria.
- Fire ants: Known for their painful stings, they are the most dangerous to human health.
- Pavement ants: Common around buildings, they can contaminate food sources.
What Research Says About Ants and Disease?
Recent studies confirm that ants can carry harmful bacteria on their bodies. For example, researchers have found ants transporting Salmonella and E. coli from waste areas to human food. This research supports the idea that ants act as vectors of bacteria, even if they don’t directly cause diseases themselves.

Additionally, ants have been shown to carry other pathogens like Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, which can lead to infections. Their ability to move quickly between unsanitary and clean areas makes them effective carriers of germs. These findings highlight the importance of controlling ant infestations to reduce health risks.
Can Ants Cause Allergies Beyond Bites?
Some people may develop allergic reactions just from exposure to ant debris, such as dead ants, ant saliva, or venom residues. Symptoms can include:
- Sneezing or a runny nose
- Skin irritation
- Eye irritation
These reactions are less common but can affect sensitive individuals.
What Research Says About Ants and Disease?
Recent studies confirm that ants can carry harmful bacteria on their bodies. For example, researchers have found ants transporting Salmonella and E. coli from waste areas to human food. This research supports the idea that ants act as vectors of bacteria, even if they don’t directly cause diseases themselves.
Additionally, ants have been shown to carry other pathogens like Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, which can lead to infections. Their ability to move quickly between unsanitary and clean areas makes them effective carriers of germs. These findings highlight the importance of controlling ant infestations to reduce health risks.
FAQS:
1. Can ants make people sick?
Ants don’t directly cause sickness but can carry harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli. When they contaminate food or surfaces, these bacteria can cause food poisoning or infections, especially in children, elderly, or people with weak immune systems.
2. What types of bacteria do ants carry?
Ants can carry various harmful bacteria including Salmonella, E. coli, Staphylococcus, Shigella, and Clostridium. These bacteria can cause foodborne illnesses and infections if transferred to food or surfaces, making ant infestations a potential health risk in homes and restaurants.
3. How do ants spread germs in the home?
Ants travel between dirty and clean areas, picking up bacteria from trash, drains, or waste and transferring them to food, countertops, and utensils. This cross-contamination can increase the chance of illness and makes controlling ants in the kitchen very important.
4. Are all ants dangerous to humans?
Not all ants pose health risks. However, some species like fire ants can bite or sting, injecting venom that causes pain, itching, swelling, and even allergic reactions. Sensitive individuals may develop infections or severe reactions from these bites or stings.
5. What is the best way to prevent ants from spreading bacteria?
To prevent bacteria from spreading, keep your home clean, store food in sealed containers, fix leaks, and remove trash promptly. Regular cleaning and professional pest control treatments are also essential to eliminate ant colonies and reduce health risks from these pests.
Conclusion:
Ants may look harmless, but they can carry harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli, which can contaminate food and increase health risks. Although ants don’t directly cause diseases, their presence in homes can lead to foodborne illnesses.
Preventing infestations by keeping your home clean, sealing food properly, and using professional pest control is important to protect your family. Some ants can also bite or sting, causing allergic reactions in sensitive people. Being aware of these risks and acting early helps maintain a safer and healthier home environment.
Related post: