Is Gum Disease Hereditary – Simple Ways To Lower Your Risk Starting Now!
Gum disease, medically known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health problem affecting millions worldwide. While poor oral hygiene and lifestyle habits such as smoking or unhealthy diets are well-known causes, emerging research shows that genetics plays a significant role in its development. This article explores how hereditary factors influence gum disease, how it progresses, and the steps you can take to protect your oral health.
By understanding the genetic links alongside environmental triggers, you can better manage your risk and maintain a healthy smile. Early detection and personalized care are crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Taking proactive steps now can help you avoid serious dental problems in the future.
What Is Gum Disease and How Does It Develop?
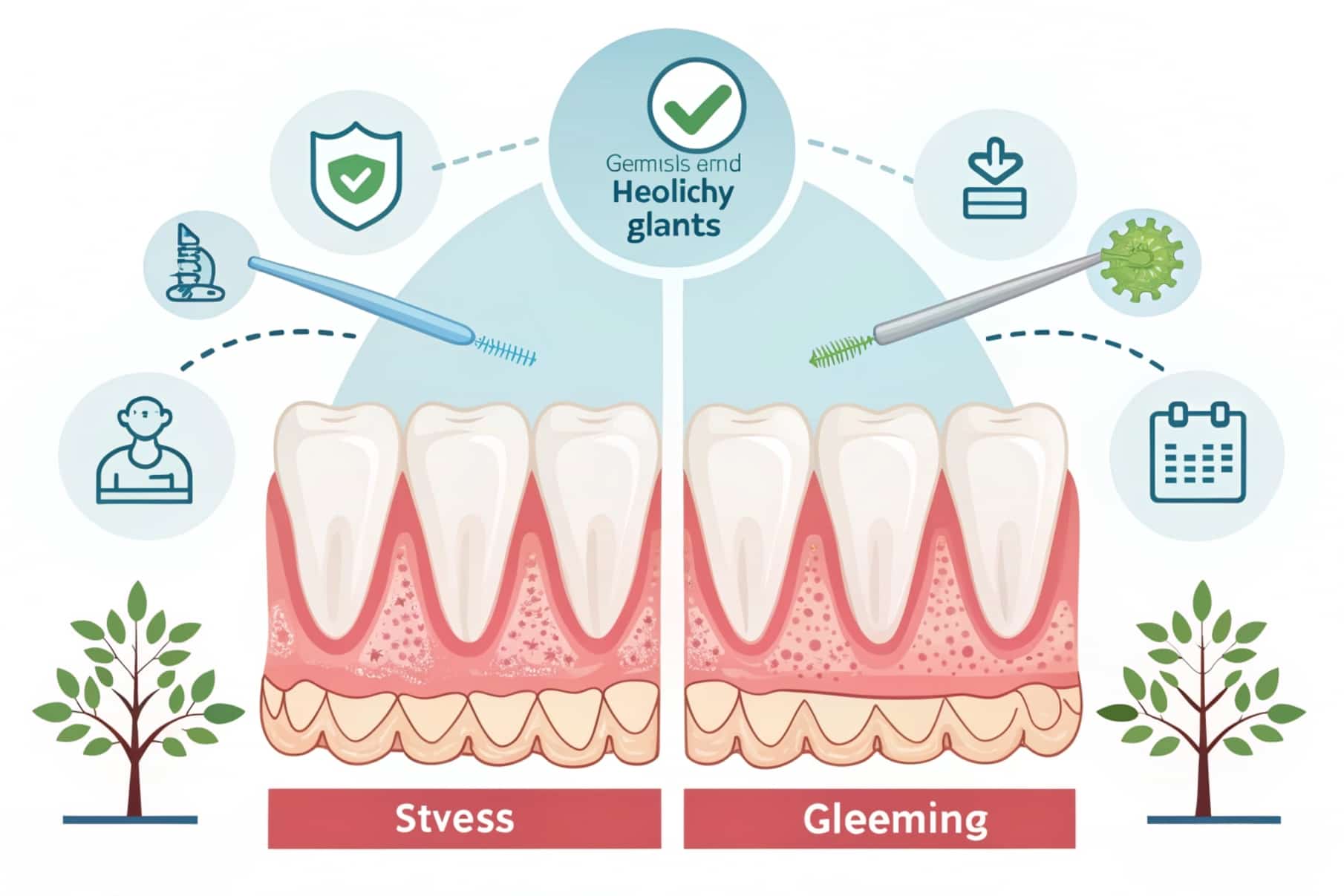
Gum disease begins with plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that builds up on teeth and gums. If plaque is not regularly removed through brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums. This irritation causes inflammation, redness, and bleeding — signs of early gum disease known as gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form where the gums and the bone supporting teeth start to break down, potentially causing tooth loss.
The process is gradual and often painless, making it easy to overlook until serious damage occurs. It’s important to understand that gum disease does not affect everyone equally, and here is where genetics come into play. gum disease is it hereditary is a common question, and the answer depends on understanding these genetic influences.The process is gradual and often painless, making it easy to overlook until serious damage occurs. It’s important to understand that gum disease does not affect everyone equally, and here is where genetics come into play.
What age does gum disease start?
Gum disease can start at any age, but early signs often appear in adolescence or early adulthood. Gingivitis, the mildest form, may begin in the teenage years due to poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, or diet. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis in adulthood, leading to serious damage to gums and bone supporting the teeth.
Regular dental check-ups, daily brushing and flossing, and professional cleanings are important at every age to prevent gum disease from developing or worsening, helping maintain healthy gums and overall oral health throughout life.
What Is Periodontal Disease and How Common Is It?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 3.5 billion people worldwide suffer from dental diseases. Severe gum disease, or periodontitis, affects nearly 10% of the global population. Diet, tobacco use, and alcohol all play major roles in many cases. However, recent research suggests genetic factors may contribute to nearly half of all periodontitis cases.
Periodontal disease is a serious infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other health complications. Maintaining good oral hygiene and getting regular dental checkups are essential steps in preventing and managing this common condition. is periodontal gum disease hereditary is a topic of growing research interest, as genetic links become clearer.
How Does Genetics Influence Gum Disease?
Scientific studies suggest that about 30% of the population carries genetic traits that affect their immune response to bacterial infections in the mouth. These genetic factors influence how the body’s immune system responds to plaque buildup and inflammation. When the immune system overreacts or underreacts due to inherited gene variations, it can lead to more severe and faster progression of gum disease.
Cytokines and Immune Response:
One key genetic factor involves cytokines, small proteins that regulate the immune system’s reaction to infection. Variations in cytokine genes can cause an improper immune response, either too weak or too aggressive. This imbalance contributes to chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and bone loss around the teeth. Research has found that people with these genetic differences are up to 20 times more likely to develop aggressive periodontitis compared to those without these traits.
How Do Cytokines Affect Gum Disease?
Cytokines are small proteins that act as messengers in the body, telling cells what to do. They’re crucial to the immune system, helping produce white and red blood cells and coordinating inflammatory responses to fight infection. When cytokine signaling is too weak or too strong, it can cause health problems.
About 30% of people have genetic variations that cause cytokine response issues. These individuals may experience chronic pain, inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and a higher risk of developing periodontitis. They can be up to 20 times more likely to develop advanced periodontitis, with earlier onset and faster progression. Managing gum disease in these patients requires special care and a personalized approach.
How Hereditary Gum Disease Differs from Other Types?
While most gum disease cases result from poor oral care and lifestyle habits, is pyria gum disease hereditary is another important question, since hereditary gum disease requires a unique approach. Even with excellent oral hygiene, those genetically predisposed may develop gum disease more easily or earlier in life.
| Factor | Hereditary Gum Disease | Non-Hereditary Gum Disease |
| Cause | Genetic immune response variations | Plaque, tartar, smoking, poor oral care |
| Age of Onset | Early, often before age 35 | Usually later in life |
| Progression Speed | Rapid and aggressive | Slow to moderate |
| Response to Treatment | May require specialized dental care | Responds well to standard dental hygiene |
| Family History | Often positive | Usually negative |
This table highlights why it is important to recognize hereditary gum disease early. People with a family history of severe gum disease should be particularly vigilant with their oral care and consider genetic testing. is gum disease hereditary uk is also a common query for those looking to understand regional awareness and healthcare approaches.
What Are the Key Signs and Indicators of Periodontal Disease?
Here are five detailed points, each written in exactly 55 words, to help you clearly understand the major signs and contributing factors of periodontal disease:
Gum Appearance and Bleeding:
Healthy gums are pink, tight, and don’t bleed during brushing or flossing. Bleeding gums are often the first visible sign of periodontal disease. Inflammation from plaque buildup causes the gums to swell and bleed easily. If not addressed early, this condition can worsen, leading to more serious gum damage and long-term oral health issues.
Tooth Mobility and Looseness:
Teeth should feel secure and not move when touched. As periodontal disease progresses, the gums and bone supporting the teeth weaken, causing teeth to loosen or shift. Even if the teeth are free of decay, bone loss around the roots can result in instability, ultimately leading to tooth loss if not treated promptly and properly.
Persistent Bad Breath:
Chronic bad breath, or halitosis, is a common symptom of periodontal disease. Bacteria trapped under the gum line produce foul-smelling toxins, which cause a persistent odor. Unlike temporary bad breath from food, this type won’t go away with brushing alone and signals underlying gum infection that requires professional cleaning and care to resolve.
Gum Recession and Sensitivity:
Gum recession occurs when gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing the roots. This often leads to increased tooth sensitivity, especially to hot, cold, or sweet foods. Receding gums are a clear sign of advancing periodontal disease and, if left untreated, can compromise the stability of your teeth and damage oral aesthetics.
Tooth Loss Risk by Age:
For individuals under 35, cavities are the main reason for tooth loss. However, after age 35, periodontal disease becomes the leading cause. Up to 75% of adults may lose teeth due to gum disease during their lifetime. Preventive care and early intervention are key to protecting long-term oral health and preventing tooth loss.
Also read: Is Degenerative Disc Disease A Disability – Find Out If You Qualify For Benefits!
How Does Genetic Testing Help Identify Gum Disease Susceptibility?
Thanks to advances in dental medicine, tests are now available to analyze your DNA for markers linked to gum disease risk. These tests typically look for variations in genes responsible for the immune system’s inflammatory response.
Benefits of Genetic Testing:
- Identify high-risk individuals early
- Customize prevention and treatment plans
- Monitor closely for early signs of disease
- Educate patients on their specific risk factors
Testing can be done at a dentist’s office or even through at-home kits. If gum disease runs in your family, genetic testing provides valuable information to take proactive steps.
Can You Get Tested for Genetic Risk of Periodontitis?
If you have gum disease or a family history of it, you can now take advantage of new DNA tests that reveal your genetic risk. These tests are available for home use or at your periodontist’s office. If multiple family members have had dental disease, testing may be a good idea. Understanding your genetic risk can help you and your dentist create a personalized prevention and treatment plan.
Early knowledge of your risk can help you take proactive steps to protect your oral health. Your dentist may recommend more frequent cleanings or specialized treatments. Discussing your results with a professional ensures you get the best strategy for managing your gum health.
What Other Risk Factors Affect Gum Disease Alongside Genetics?
Gum disease is influenced not just by genetics but also by various lifestyle and health factors. Tobacco use, including smoking and vaping, can damage gums and worsen the condition. A poor diet lacking essential nutrients weakens the immune system, making it harder to fight infections. Chronic illnesses like diabetes affect healing and gum health.

Hormonal changes during pregnancy or puberty, high stress levels, and certain medications that reduce saliva or impact gums also play a role. Managing these factors can greatly reduce the risk, even for those with genetic susceptibility. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene are essential in controlling gum disease. Early intervention can prevent the progression of the disease. Taking care of your overall health supports healthier gums and teeth.
Preventive Measures for Those at Genetic Risk – Easy Steps to Protect Your Gums Now!
While heredity is beyond one’s control, there are proven ways to prevent or slow down gum disease progression:
Daily Oral Hygiene Habits:
Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps remove harmful plaque that causes gum disease. Flossing daily reaches the spaces between teeth where brushes can’t, preventing buildup and inflammation. Consistent oral hygiene is essential for controlling bacteria, reducing gum irritation, and protecting your gums, especially if you have a family history of gum disease.
Regular Dental Check-ups:
Seeing your dentist regularly is crucial for maintaining healthy gums. Professional cleanings remove tartar that brushing and flossing can’t reach. Early dental exams can catch signs of gum disease before it becomes serious. If you have a genetic risk, frequent dental visits help monitor your gum health and allow timely treatments to prevent disease progression.
Lifestyle Choices to Support Gum Health:
Avoiding tobacco products, including smoking and vaping, is important since they weaken gum tissue and slow healing. Limiting alcohol intake also helps reduce irritation and dryness. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D strengthens your immune system and promotes gum repair, helping your body fight infections that can worsen gum disease.
Managing Stress for Better Gum Health:
High stress levels can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight infections, including those affecting your gums. Using relaxation methods like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can lower stress. Regular exercise also boosts immunity and improves circulation, supporting healthier gums and reducing the risk of gum disease, especially in genetically susceptible individuals.
Also read: Does Coeliac Disease Cause Weight Gain – Expert-Backed Guide You Can Trust!
How Gum Disease Affects Overall Health?
Gum disease affects more than just your mouth; it can impact your overall health. Chronic inflammation from periodontitis is connected to serious health issues like heart disease and stroke. It can also worsen complications related to diabetes and increase the risk of respiratory infections. Additionally, gum disease may lead to pregnancy problems, including preterm birth.
Because of these serious risks, preventing and treating gum disease early is essential, especially for people with a genetic predisposition. Taking care of your gums helps protect your whole body’s health.
Hereditary Gum Disease at a Glance – Essential Insights for Better Care!
| Aspect | Details |
| Prevalence | Affects roughly 10% of the population |
| Genetic Link | Present in about 30% with immune gene variations |
| Disease Onset | Often early, before age 35 |
| Progression | Rapid, more aggressive |
| Testing | Available via dental clinics and home kits |
| Prevention | Good oral hygiene, lifestyle management |
| Treatment | Deep cleaning, antimicrobial therapy, and surgery |
| Health Impact | Increased risk of systemic diseases |
How Does Periodontitis Progress and Why Is Treatment Important?
Here are the key points, each explained clearly in 55 words:
Plaque Turns Into Tartar:
When plaque is left untreated, it hardens into tartar that builds above and below the gum line. Tartar harbors bacteria that irritate the gums, making it difficult to remove with brushing alone. As bacteria multiply, they begin to trigger inflammation, creating the foundation for periodontal disease and potential long-term damage to the gums and bone.
Chronic Inflammation Damages Tissue:
Your immune system responds to gum infection with inflammation, trying to fight harmful bacteria. However, prolonged inflammation begins to break down healthy gum tissue and bone that hold your teeth in place. This self-destructive immune response leads to gum recession, bone loss, and deep pockets around the teeth, which worsen without proper dental treatment.
Also read: Coach Yplostylia Varkonin Health – Real Results, Real Wellness!
Future Directions in Gum Disease Research – Latest Breakthroughs and What to Expect!
Future research on gum disease is focused on understanding its genetic roots to create personalized treatments. Scientists are studying ways to adjust cytokine responses with new medications, aiming to reduce harmful inflammation. Gene therapy is being explored to fix immune system imbalances that contribute to gum problems.
Researchers are also working on improved diagnostic tools to detect gum disease earlier and more accurately. As this knowledge advances, people with a genetic risk for gum disease could soon receive treatments tailored specifically to their genetic makeup, improving prevention and care outcomes.
FAQs:
Can gum disease be passed down through families?
Yes, gum disease can be hereditary. Certain genes affect how your body responds to bacteria, increasing the chance of gum problems. If close family members have gum disease, your risk may be higher. However, genetics is just one factor among many that influence gum health.
Does having a family history mean I will get gum disease?
No, having a family history increases your risk, but it doesn’t guarantee you will get gum disease. Good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and healthy lifestyle habits can reduce your chances. Early care and prevention are key to managing genetic risks effectively.
Are genetic tests available to check my risk for gum disease?
Yes, genetic testing can identify if you have genes linked to gum disease susceptibility. These tests help dentists understand your risk better and create personalized treatment plans. However, genetic testing is just one part of overall gum health assessment.
How can I reduce my chances of gum disease if it runs in my family?
Maintain excellent oral hygiene by brushing twice daily and flossing. Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. Avoid tobacco, eat a balanced diet, and manage stress. These steps can help control gum disease risk, even if it runs in your family.
Is hereditary gum disease more severe than other types?
Hereditary gum disease can sometimes be more aggressive and progress faster than non-genetic forms. Early detection and treatment are important to prevent serious damage. Working closely with a periodontist who understands genetic factors can help manage the disease more effectively.
Conclusion:
Gum disease can be hereditary, meaning genetic factors play a significant role in how likely you are to develop it. While family history increases risk, good oral hygiene and regular dental care remain essential for prevention. Understanding your genetic risk through testing and working closely with your dentist can help manage the condition early.
By combining proper daily habits with professional guidance, you can protect your gums and overall health, even if you have a genetic predisposition to gum disease. Early intervention and lifestyle changes are key to slowing disease progression. Staying informed empowers you to take control of your oral health for life.
Related post: